2018 MPE project by Heaton Rhodes
The mounting method of an acceleration sensor to an asset is a critical factor for sensor unit reliability as the transfer of momentum occurs directly through the mount. Despite this, sensor mounting has been largely overlooked in academic and commercial research, particularly for micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) accelerometers. This thesis compares the effects of different mounting mechanisms for MEMS based sensor units.
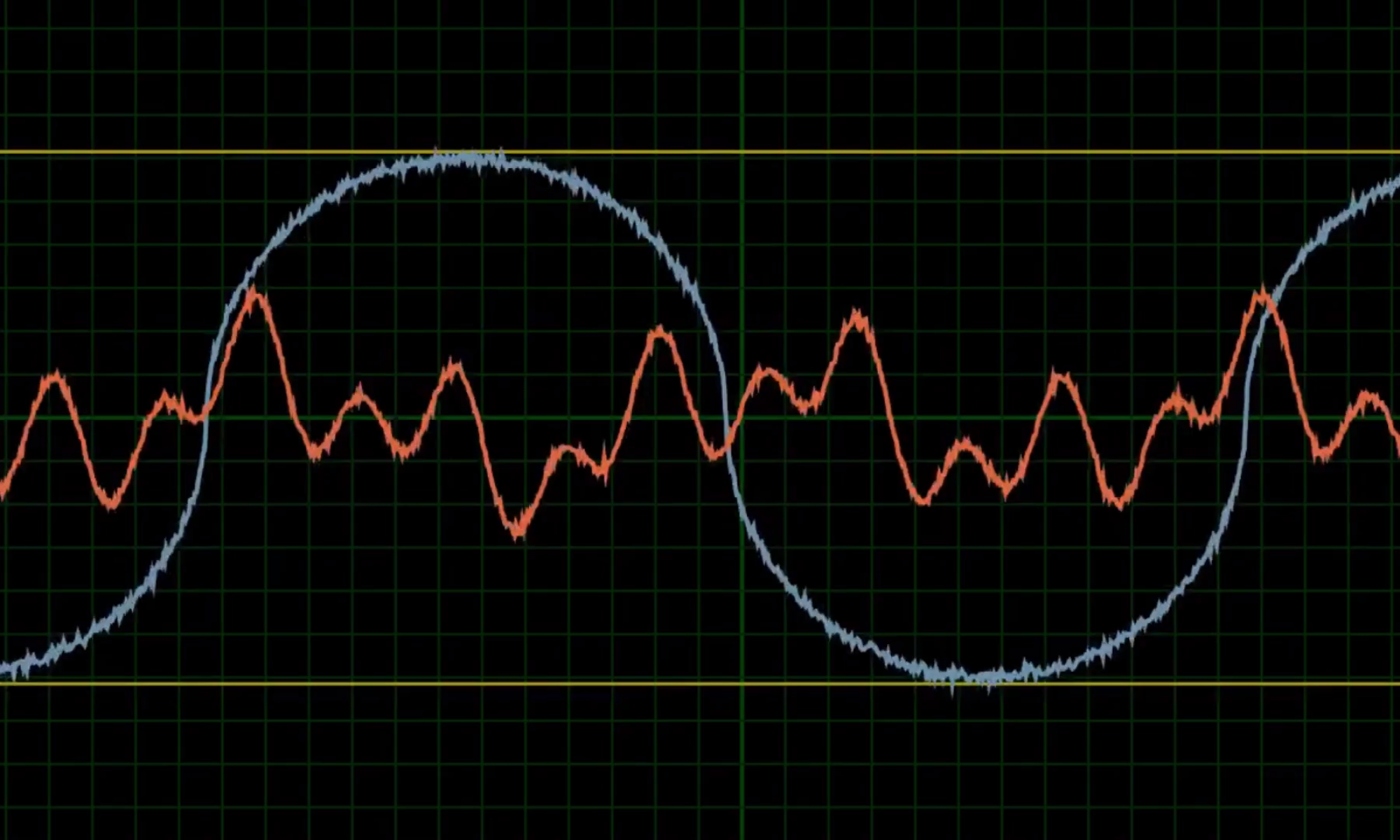
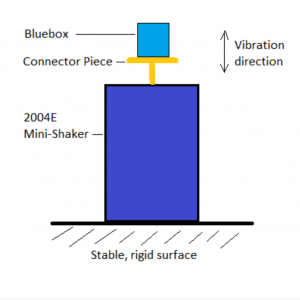
The UWA Systems Health Lab is investigating the potential of low-cost sensor units in the condition monitoring industry and has developed the “Bluebox”. The Bluebox streams data from a MEMS accelerometer via a WiFi-enabled microcontroller. The Bluebox costs roughly $50, while commercially available MEMS sensors begin at $500. These low-cost sensor units will reduce the cost of data collection in the condition monitoring industry. The Bluebox design was modified to facilitate six mounting methods, and compared to a commercial MEMS sensor unit, the Slamstick, with four mounting methods. The response of these units to vertical linear vibration was tested using a shaker to identify the response characteristics of each mounting method.